Video Examples of Baby-Toddler Noises, and Speech 24-60 Months
Vegetative Sounds
Vegetative sounds relate to bodily functions: digestion, excretion and respiration. The sounds include burps, coughs, hiccups, sneezes, gulps, grunts, etc.
Fixed signals
Fixed signals are recurring motor sequences that do not vary across individuals (or languages: a giggle will never sound as though the giggler speaks a particular language). Fixed signals include laughs, giggles, cries, and moans, etc.
Protophones
The purpose of protophones varies. They can be "just for fun", to attract attention, etc. Protophones are speech-like, but not "transcribable"; that is, they cannot be written down using phonetic symbols (IPA | Extended IPA for transcribing disordered speech). Protophones include quasivowels (vowel-like sounds produced with the vocal tract at rest) and marginal babbling (sometimes called pre-canonical babbling). It is similar to cooing where the infant produces a few random sounds.
12 months: Typical development
Resonant Productions
Fully resonant productions are "transcribable"; that is, they can be written down using phonetic symbols (IPA | Extended IPA for transcribing disordered speech). Resonant productions include fully resonant vowels, resonant consonants, canonical babbling and true words.
14 months: Typical development
Canonical Babbling: Typical development
Variegated Babbling: Typical development
Speech
"Speech" can include meaningful speech (real words) or non-words (made-up words)
24 months made-up words: Typical development
30 months: Typical development
37 months: children talking to each other on the phone: Typical development
48 months: telling a story (1): Typical development
48 months: telling a story (2): Typical development
60 months: A 5-year-old asks Siri a series of questions: Typical development
Link
Typical speech and language development in infants and young children
Citation
Cite this page as: Bowen, C. (2020). Video Examples of Baby-Toddler Noises, and Speech 24-60 Months. Retrieved from http://www.speech-language-therapy.com/ on [insert the date that you retrieved the file here].
References
Bowen, C. (2015). Children's Speech Sound Disorders (2nd ed.). Oxford, Wiley-Blackwell, page 82.
Oller, K. D., Eilers, R. E., Neal, R. & Schwartz (2019). Precursors to speech in infancy: The prediction of speech and language disorders. Journal of Communication Disorders, 32(4), 223-245.
Ramsdell, H. L., Oller, D. K., & Ethington, C. A. (2007). Predicting phonetic transcription agreement: insights from research in infant vocalizations. Clinical linguistics & phonetics, 21(10), 793–831.
CPD - Sound Reasoning - the "Lighthouse Page"
This is the Lighthouse Page It contains links to information and resources mentioned in Sound Reasoning. The CPD event Sound Reasoning was replace by Treatment Targets and Strategies in October 2023, for CPD events in 2023-2024.
CPD - Resources

The CPD Resources page contains links to product pages for resources mentioned in Continuing Professional Development (CPD) events with Caroline Bowen. There are also articles of interest and a small selection of intervention materials to download. Other resources link from the Resources Tab at the top of every page of this site.
To become a member of the the private Facebook Group, International Speech Sound Disorders Discussion for SLPs/SLTs (E3PBforSSD) click "Join Group", HERE, and answer three questions.
The CPD Events page comprises a listing of past and forthcoming presentations by Caroline Bowen.
CPD Information for Potential Hosts
CPD Information for Potential Hosts
The CPD Information for Potential Hosts page contains a list of available presentations ("training") with outlines and learner objectives. These range from 1-hour talks, to study days, to 2-day or 3-day presentations, to longer courses. Further information (speakers' fee, AV request, travel and accommodation costs, cancellation policy, etc.) is available, in the Information for Potential Hosts document, on request. e-mail. Please note that this informaton is not available online.
CPD Resources
See below.
Assessment
- Child Speech Assessment Resources [THIS SITE]
- Diagnostic Evaluation of Articulation and Phonology (DEAP)
- Phonetic and Phonological Systems Analysis (PPSA)
- Toddler Phonology Test (TPT)
Charts and diagrams
Please avoid downloading the same file multiple times as it increases my bandwidth usage and drives up my costs. Choose a pdf or pptx file; download it once, and save it to a folder. If you find the free resources here useful, and would like to make your secure donation to the maintenance of this site, please click here, and then click on the DONATE BUTTON.
Consonant charts
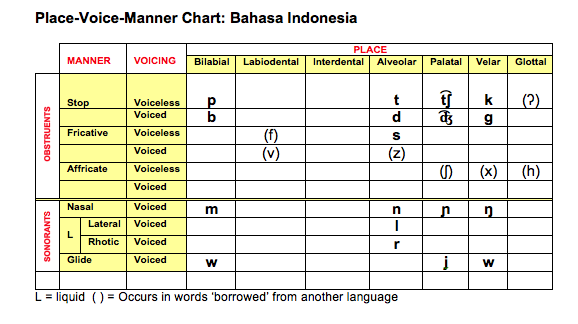
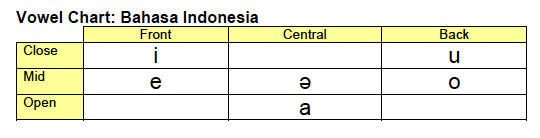
Bahasa Indonesia (Indonesian)
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart and Vowel Chart: Bahasa Indonesia .pdf
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: Bahasa Indonesia .png
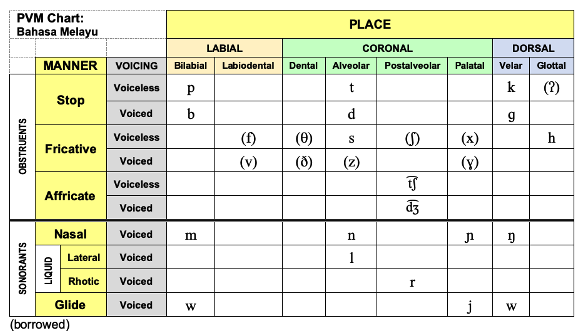
Bahasa Melayu (Malaysian)
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: Bahasa Melayu.png
Bangla
Place-Aspiration-Voice (PAM) Chart: Bangla.pdf
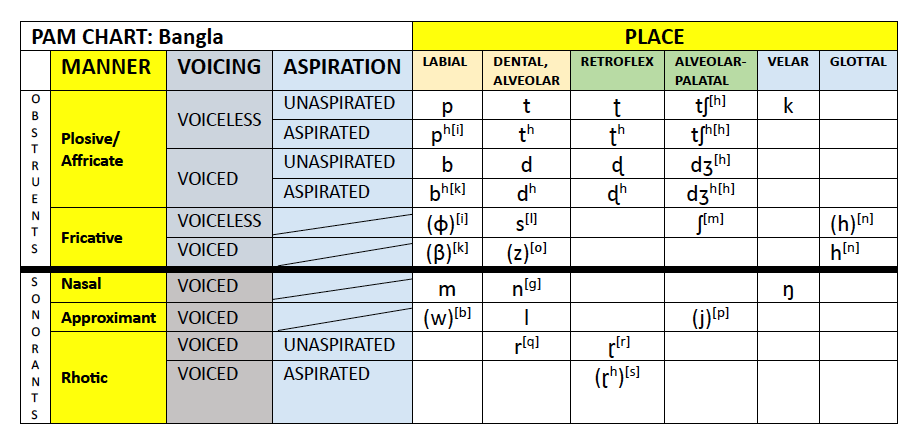
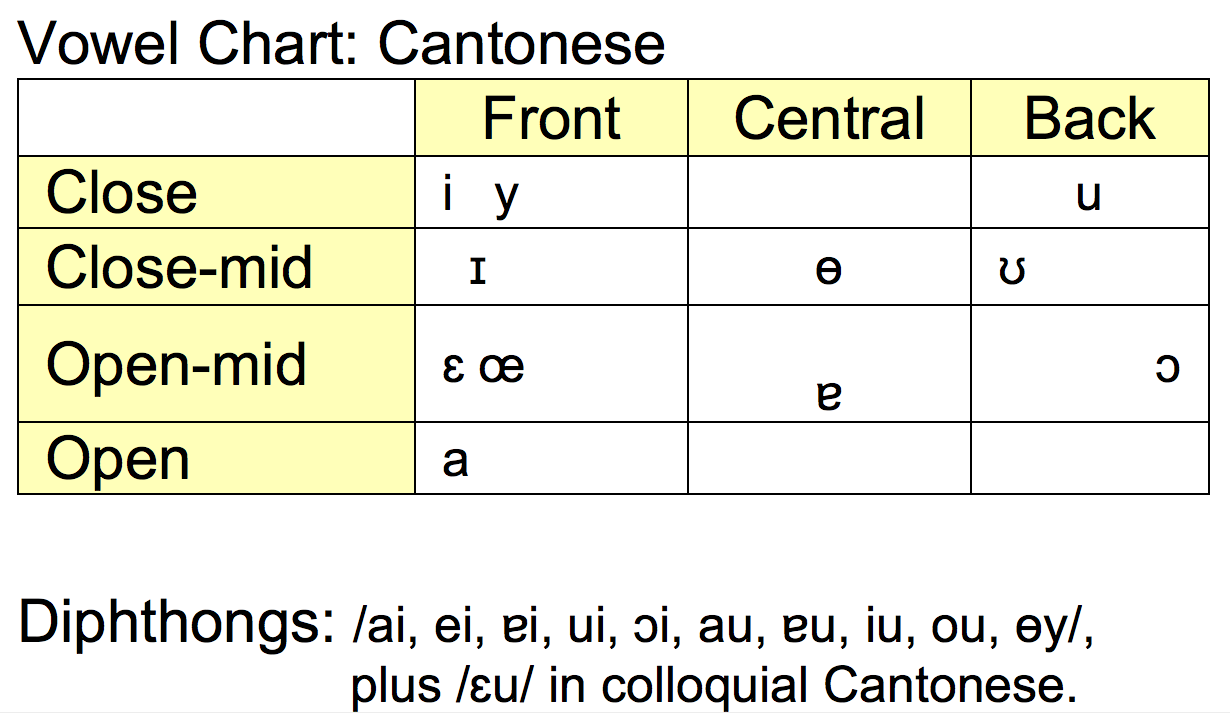
Cantonese
Place-Aspiration-Manner (PAM) Chart: Cantonese .png
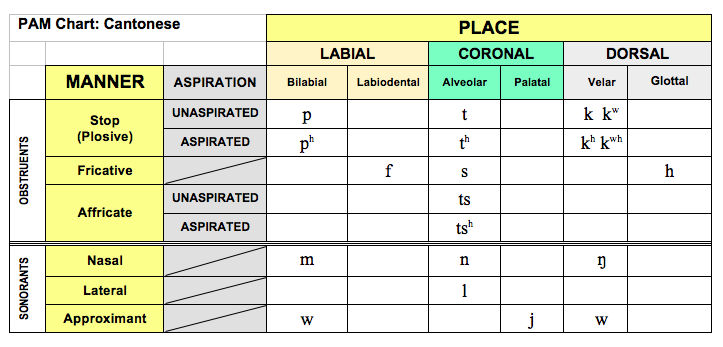
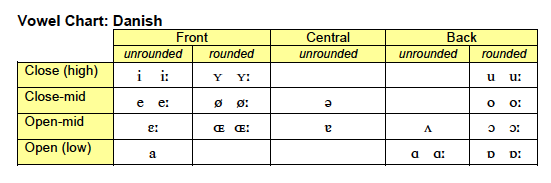
Danish
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart and Vowel Chart: Danish .pdf
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: Danish .png
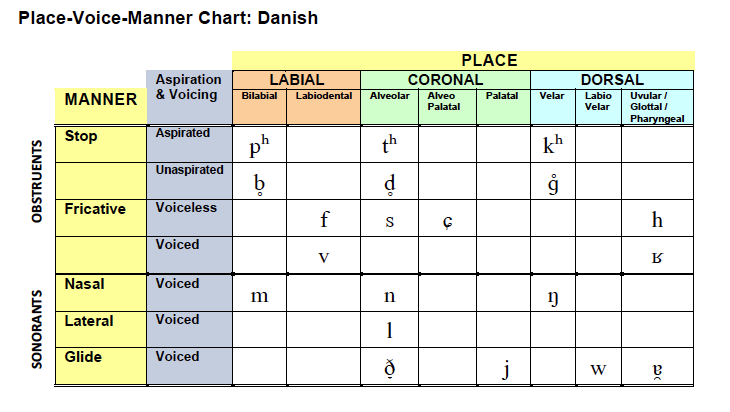
English
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: English .png

Icelandic
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: Icelandic .pdf
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: Icelandic .png
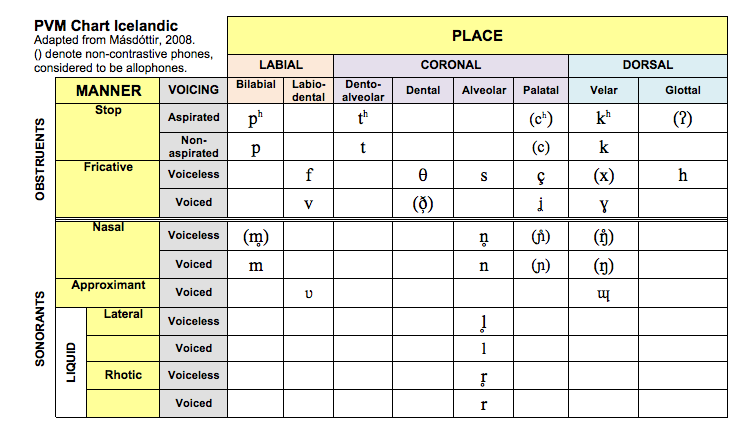
Másdóttir, T. (2008). Phonological development and disorders in Icelandic-speaking children. Unpublished doctoral dissertation. University of Newcastle.
Irish
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: Irish - two charts .pdf
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: Irish - two charts .png
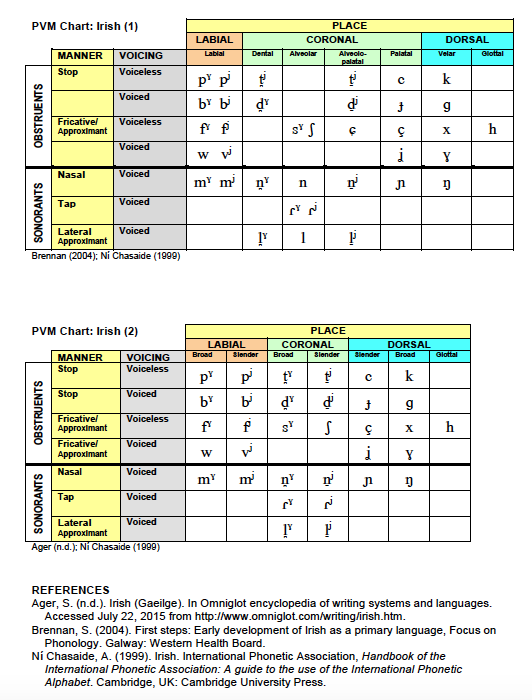
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: Irish - Chart 1 .png
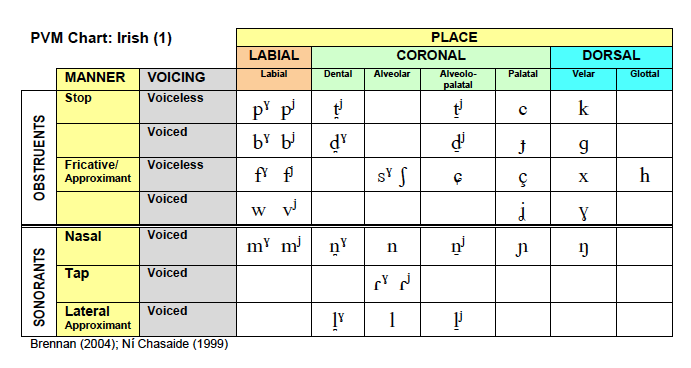
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: Irish - Chart 2 with columns for broad and slender consonants .png
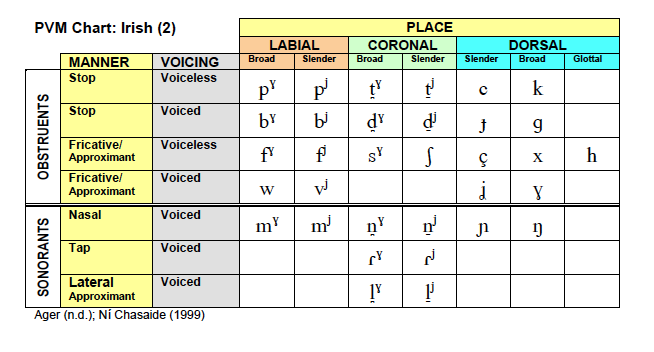
Norwegian
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM): Norwegian .png
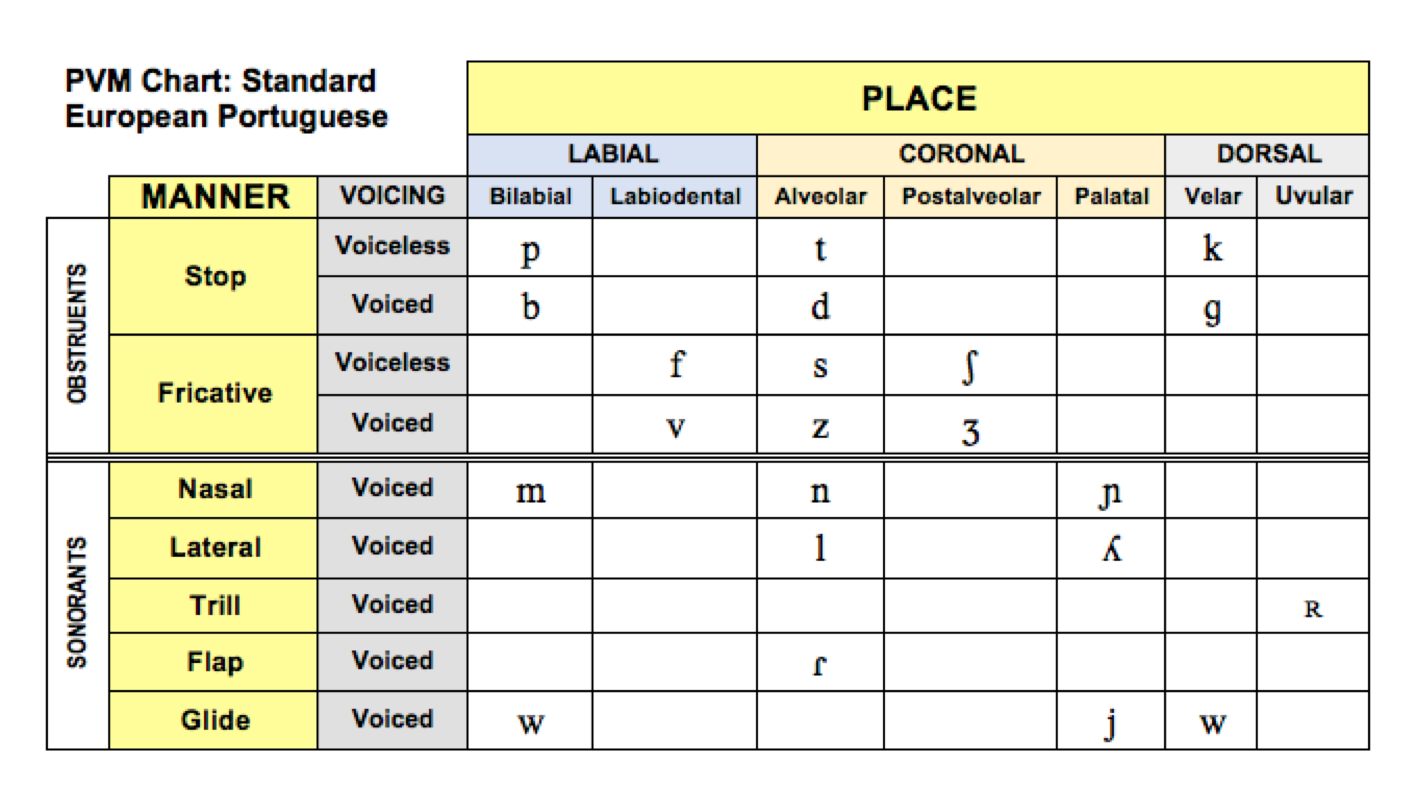
Portuguese
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: Portuguese .png
Tagalog
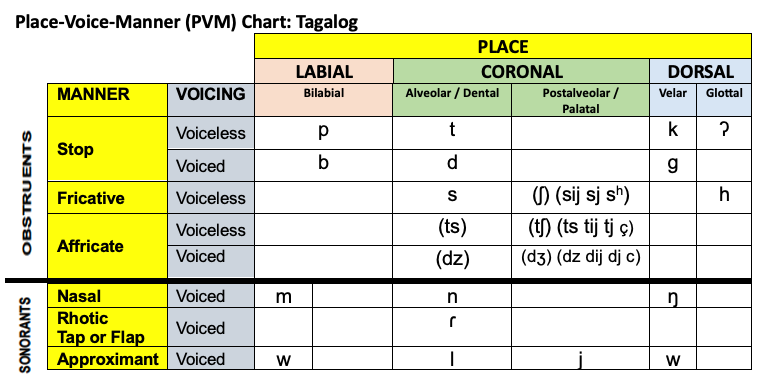
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: Tagalog.png
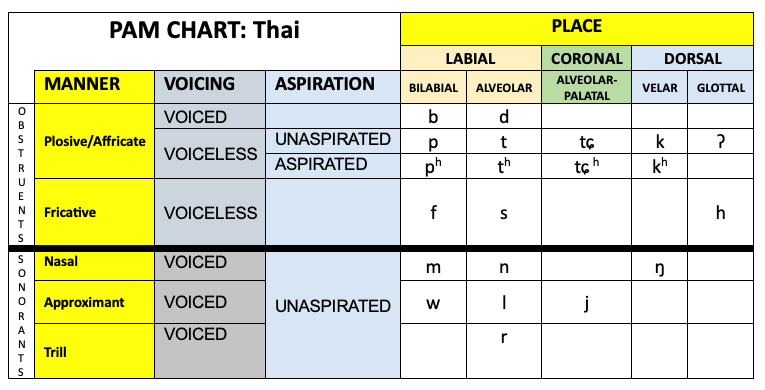
Thai
Place-Aspiration-Manner (PAM) Chart: Thai.png
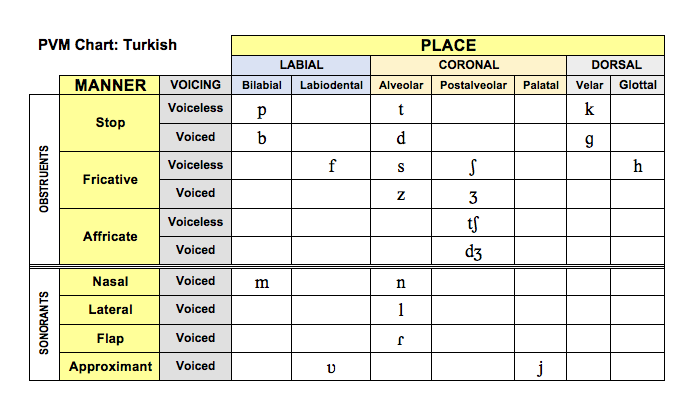
Turkish
Place-Voice-Manner (PVM) Chart: Turkish .png
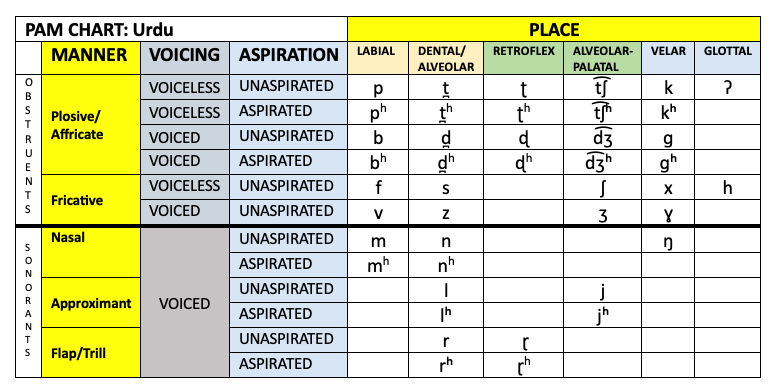
Urdu
Place-Aspiration-Manner (PAM) Chart: Urdu.png
Farooq, M., & Mahmood, A. (2021). The Acoustic Effect of Urdu Phonological Rules on English Speech. Linguistics and Literature Review, 7(1), 83-97. https://doi.org/10.32350/llr.71.07 (PDF)
Vowel charts
Vowel chart: Bahasa Indonesia .png
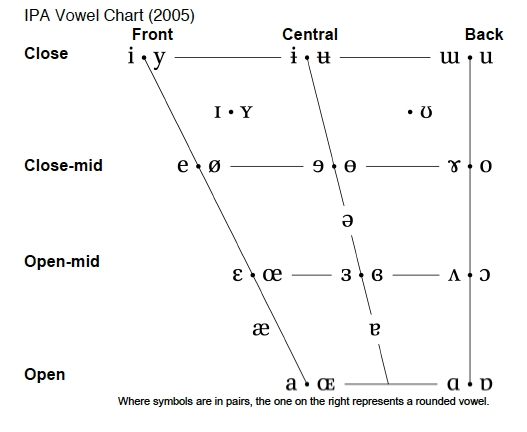
Vowel symbols for broad transcription of Australian English .pdf
Vowel symbols for broad transcription of Australian English .png

Speech Sound Disorders Umbrella

Intervention materials - free resources
Please avoid downloading the same file multiple times as it increases my bandwidth usage and drives up my costs. Choose a pdf or pptx file; download it once, and save it to a folder. If you find the free resources here useful, and would like to make your secure donation to the maintenance of this site, please click here, and then click on the DONATE BUTTON.
- Einstein (6) [THIS SITE]
- Einstein (20) [THIS SITE]
- Miccio Character Cards 7 pages - Updated 2012 [THIS SITE]
- Pigs in Hiding (video)
- Resources Index [THIS SITE]
Interventions - free resources

The "Lighthouse Page" for "Sound Reasoning"
Articles
Please read this before downloading pdf or pptx files
Please avoid downloading the same file multiple times as doing so increases my bandwidth usage and drives up the cost of maintaining this site. Choose a pdf or pptx file; download it once, and save it to a folder.
ASHA (2007). Position Statement on Childhood Apraxia of Speech. WEB VERSION | PDF VERSION
ASHA (2007). Technical Report on Childhood Apraxia of Speech. WEB VERSION | PDF VERSION
Baker, E. (2004). Phonological analysis, summary and management plan. ACQuiring Knowledge in Speech, Language and Hearing, 6(1), 14-21. Copyright 2004 Speech Pathology Australia. Uploaded by permission. part 1 and part 2
Barlow, J. A., and Gierut, J. A. (2002). Minimal pair approaches to phonological remediation. Seminars in Speech and Language, 23(1), 57-67. Click here and Click here (important to read both of these)
Bernhardt, B., & Major, E. (2005). Speech, language and literacy skills 3 years later: A follow-up study of early phonological and metaphonological intervention.International Journal of Language and Communication Disorders, 40, 1-27. Click here
Betz, S. K. & Stoel-Gammon, C. (2005). Measuring articulatory error consistency in children with developmental apraxia of speech. Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics. January-February, 53-66. Click here
Crosbie, S., Holm, A. & Dodd, B. (2005). Intervention for children with severe speech disorder: A comparison of two approaches. International Journal of Language and Communication Disorders, 40, 467 - 491. Click here
Davis, B.L. & Velleman, S.L. (2000). Differential Diagnosis and Treatment of Developmental Apraxia of Speech in Infants and Toddlers.Infant Toddler Intervention: The Trans-disciplinary Journal, 10(3), pp. 177 - 192. Click here LARGE FILE - opens in a new window
Finn, P. Bothe, A. & Bramlett, R. (2005, August). Science and pseudoscience in communication disorders: Criteria and applications. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 14, 172-186. Click here
Hodson, B. W. (2006). Identifying phonological patterns and projecting remediation cycles: Expediting intelligibility gains of a 7 year old Australian Child. Advances in Speech-Language Pathology, 8(3), 257 - 264. Copyright 2006 Speech Pathology Australia. Uploaded by permission. Click here
Maassen B. (2002). Issues contrasting adult acquired versus developmental apraxia of speech. Seminars in Speech and Language. 23(4), 257-266. Click here
Miccio, A. W., Elbert, M., & Forrest, K. (1999). The Relationship Between Stimulability and Phonological Acquisition in Children With Normally Developing and Disordered Phonologies. American Journal of Speech-Language Pathology, 8, 347-363. Click here
Murray, E., McCabe, P., & Ballard, K. (2012) A comparison of two treatments for childhood apraxia of speech: methods and treatment protocol for a parallel group randomised control trial BMC Pediatrics 12:112. Click here
Peppe, S. and McCann, J. (2003). Assessing intonation and prosody in children with atypical language development: the PEPS-C test and the revised version. Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics, 17/4-5, 345-354. Click here
Peter, B. and Stoel-Gammon, C. (2005). Timing errors in two children with suspected childhood apraxia of speech (sCAS) during speech and music-related tasks. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics, 19(2), 67-87. Click here
Royal College of Speech and Language Therapists (2011). RCSLT Position Paper on Developmental Verbal Dyspraxia, Author. (RCSLT, 2011).
Rvachew, S., Hodge, M., & Ohberg, A. (2005). Obtaining and Interpreting Maximum Performance Tasks from Children: A Tutorial. Journal of Speech Language Pathology and Audiology, 146-157. Click here
Shriberg, L.D., Campbell, T.F., Karlsson, H.B., McSweeney, J.L., Nadler, C.J. (2003). A diagnostic marker for childhood apraxia of speech: The lexical stress ratio. Clinical Linguistics and Phonetics, 17(7), 549-574. Click here
Shriberg, L. D., Kent, R. D., Karlsson, H. B., McSweeny, J. L., Nadler, C. J., & Brown, R. L. (2003). A diagnostic marker for speech delay associated with otitis media with effusion: backing of obstruents. Clinical Linguistics & Phonetics, 17(7), 529 - 547. Click here
Stackhouse, J., Wells, B., Pascoe, M., & Rees, R. (2002). From phonological therapy to phonological awareness. Seminars in Speech and Language, 23(1), 27-42. Click here
Velleman, S. (2002). Phonotactic therapy. Seminars in Speech and Language, 23, 43-57. Click here
Waisman Phonology Project Publications and Presentations
Watts, N. (2004). Assessment of vowels summary. ACQuiring Knowledge in Speech, Language and Hearing (ACQ), 6(1), 22-25. Speech Pathology Australia. Uploaded by permission. Click here
Williams, A. L. (2003). Letter to the editor: On Minimal Pair Approaches to Phonological Remediation. Seminars in Speech and Language, 24(3), 257-258. Click here
CPD - Information for Potential Hosts and Participants
About the presenter
Caroline Bowen AM, PhD, CPSP, ASHA Fellow, Life Member SPA, Hon FRCSLT
Dr Caroline Bowen practiced in Australia as a clinical speech-language pathologist from 1969 to 2011. Since 2005 she has presented invited Continuing Professional Development (CPD) in Australia, Canada, Denmark, Éire, England, Hong Kong, Iceland, India, Indonesia, Malaysia, New Zealand, Northern Ireland, Norway, Pakistan, the Philippines, Portugal, Scotland, Singapore, South Africa, Turkey and the US. And she would like to do a little bit more before retirement in December 2024. Read about Caroline Bowen here, or in Wikipedia.
Choosing an event in 2024
Children’s Speech
The child speech events are informed by Bowen (2023) Children’s Speech Sound Disorders, 3rd edition (which is available worldwide via the publisher, Wiley-Blackwell, or via Amazon, and more recent literature. The three events are:
-
A 1-day event which can be expanded into a more detailed 2-day event
Streamlining Assessment and Intervention for Children’s Speech Sound Disorders OUTLINE and OBJECTIVES -
A 2-day or 3-day event
Addressing Children’s Speech Sound Disorders: What’s Under the Umbrella? OUTLINE and OBJECTIVES -
A 1-day or more detailed 2-day event based on Chapters 4, 7 and 9 of Bowen, 2023
Treatment Targets and Strategies OUTLINE and OBJECTIVES
Evidence-based and non-evidence-based practice
The events relating to science, pseudoscience, and treatment fads in allied health and education practice are based on Bowen and Snow, 2017 and two more books in preparation for J&R Press. They are the second edition of the 2017 book, and a new one: The Developmental Disorders Roadmap. The two presentations are as follows.
-
A 1-day event
Honing Our Information and Research Literacy Skills in the ‘Fake News’ Era ABSTRACT and OBJECTIVES -
A 1-day event
Science and Pseudoscience in the Clinic and Classroom OUTLINE and OBJECTIVES
Session Times
All one, two and three day events are based on 375 minutes of presentation time per day. The timetables are open to negotiation. Please let the presenter know well in advance which you prefer, and also whether you wish to alter in any way the one you have chosen. Note that the lunch break cannot be fewer than 45 minutes.
Timetable 1 - 9:00 am - 5:00 pm
TIMETABLE 1 IS THE PREFERRED TIMETABLE FOR ALL EVENTS
Registration: 8:30 am for a 9:00 am start
Session 1: 9:00-10:45 (105 minutes)
Tea Break: 10:45-11:15 (30 minutes)
Session 2: 11:15-12:45 (90 minutes)
Lunch Break: 12:45-1:45 (60 minutes)
Session 3: 1:45-3:15 (90 minutes)
Short Tea Break: 3:15-3:30 (15 minutes)
Session 4: 3:30-5:00 (90 minutes)
Finish: 5:00 pm
Total presentation time: 375 minutes
Timetable 2 - 9:15 am - 5:00 pm
Registration: 8:45 am for a 9:15 am start
Session 1: 9:15-11:00 (105 minutes)
Tea Break: 11:00-11:30 (30 minutes)
Session 2: 11:30-1:00 (90 minutes)
Lunch Break: 1:00-1:45 (45 minutes)
Session 3: 1:45 - 3:15 (90 mins)
Short Tea Break: 3:15-3:30 (15 minutes)
Session 4: 3:30-5:00 (90 minutes)
Finish: 5:00 pm
Total presentation time: 375 minutes
Timetable 3 - 9:00 am - 4:45 pm
Registration: 8:30 am for a 9:00 am start
Session 1: 9:00-10:45 (105 minutes)
Tea Break: 10:45-11:15 (30 minutes)
Session 2: 11:15-12:45 (90 minutes)
Lunch Break: 12:45-1:30 (45 minutes)
Session 3: 1:30-3:00 (90 minutes)
Short Tea Break: 3:00-3:15 (15 minutes)
Session 4: 3:15-4:45 (90 minutes)
Finish: 4:45 pm
Total presentation time: 375 minutes
The following documents are available on request
Information for Potential Hosts (includes speaker fees, travel arrangements, insurance, accommodation, etc.)
Handout Printing and Distribution Instructions
AV Information for Potential Hosts (includes IT requirements, room setup, technical support, etc.)
PAST EVENTS
CPD Events for 2022
(1) SSD101: Introduction to Speech Sound Disorders in Children
ABOUT THIS 1-DAY EVENT, new in 2015 and progressively updated for 2016-2021
Bowen (2015) is a book that covers all aspects of Children’s Speech Sound Disorders (SSD) from ‘the basics’ to the non-so-basic. This introductory CPD event focuses primarily on ‘the basics’ with reference to the book. It is designed for experienced and novice SLPs/SLTs and SLP/SLT Students seeking an uncomplicated overview of the classification, assessment, differential diagnosis, treatment target selection, and intervention for articulation and phonological disorders and childhood apraxia of speech (developmental verbal dyspraxia). It is also suitable as a refresher for SLPs/SLTs re-entering the profession, those making the switch from ‘adult’ to ‘child’ work, and those who feel rusty in relation to the connections between theory, evidence and practice.
Assuming little prior knowledge of the peer-reviewed literature on phonological principles, complexity principles, principles of motor learning, and key developments in the last 10 to 15 years in child speech assessment and intervention, it is aptly dubbed SSD101.
REFERENCE
Bowen, C. (2015). Children's Speech Sound Disorders (2nd ed). Oxford, Wiley-Blackwell.
(2) The Assessment and Treatment of Children with Phonological Impairment
ABOUT THIS 1-DAY EVENT, new in 2015, and progressively updated for 2016-2021
'The Assessment and Treatment of Children with Phonological Impairment' is a 1-day professional development event designed for experienced through to novice Speech-Language Pathologists / Speech and Language Therapists, and SLP/SLT Students. It is also suitable as a refresher for SLPs/SLTs re-entering the profession, those making the switch from ‘adult’ to ‘child’ work, and those who feel rusty in relation to the connections between phonological theory, evidence and practice.
The range of evidence-based and/or theoretically sound intervention approaches SLPs/SLTs employ to work with children with SSD is extensive. They include: Auditory Input Therapy / Naturalistic Intervention, Core Vocabulary Therapy, the Cycles Phonological Patterns Approach, Dynamic Temporal and Tactile Cueing (DTTC)*, Imagery Therapy, Integral Stimulation*, Metaphon, Parents and Children Together (PACT), Perceptually based intervention, Phoneme Awareness Intervention, Phonemic Intervention including four minimal pair approaches, Phonetic Intervention / Articulation Therapy, Psycholinguistic Intervention, Rapid Syllable Transition Training (ReST)*, Stimulability Therapy, The Multisensory Approach*, The Nuffield Centre Dyspraxia Programme*, and Vowel Remediation.
These intervention approaches are described in detail in Bowen (2015). There are too many to cover in detail in one, or even two days, so Dr Bowen will work with hosts to choose their preferred interventions to meet the learning needs of participants, along with the assessment procedures and target selection strategies that are congruent with the chosen intervention approaches.
NOTE RE INTERVENTIONS FOR CAS/DVD*
Interventions for Childhood Apraxia of Speech (CAS) / Developmental Verbal Dyspraxia (DVD) are not included in this 1-day event on children with phonological impairment. The interventions for CAS/DVD, marked with an asterisk above, are: Dynamic Temporal and Tactile Cueing (DTTC), Integral Stimulation, Rapid Syllable Transition Training (ReST), The Multisensory Approach and The Nuffield Centre Dyspraxia Programme. They are covered in CPD event (3), described below.
REFERENCE
Bowen, C. (2015). Children's Speech Sound Disorders (2nd ed). Oxford, Wiley-Blackwell.
(3) The Assessment and Treatment of Childhood Apraxia of Speech
ABOUT THIS 1-DAY or 2-DAY EVENT, new in 2015 and progressively updated for 2016--2021
An earlier version of 'The Assessment and Treatment of Childhood Apraxia of Speech' was presented 17 times nationally in Australia and internationally, between 2012 and 2014. This newer, updated and expanded version can be run as a 1-day event, or as a more interactive, in-depth, slower-paced 2-day event. The focus of the day, or days, is Childhood Apraxia of Speech (called Developmental Verbal Dyspraxia in the UK and defined somewhat differently from CAS), covering Classification, Assessment, Treatment Principles, Target Selection, Treatment Approaches, and practical intervention techniques and strategies.
This CPD offering was designed with experienced through to novice clinical Speech-Language Pathologists/Speech and Language Therapists, SLP/SLT Clinical Educators and Instructors, and SLP/SLT Students in mind.
(4) Sound Reasoning: Therapy Targets and Techniques for Children with Speech Sound Disorders
TABOUT THIS 1-DAY EVENT, progressively updated for 2016-2021
'Sound Reasoning: Therapy Targets and Techniques for Children with Speech Sound Disorders' was originally developed in 2014-2015 and presented in many locations worldwide. It was revised and updated for 2016, and "tweaked" progressively in response to the current literature. It focuses on what clinicians actually 'work on' in therapy sessions, and covers:
- Assessment procedures upon which to base treatment target selection choices
- Intervention principles for phonetically-based ('articulatory') error-types
- Intervention principles for phonemically-based ('phonological') error-types
- Intervention principles for motorically-based (CAS/DVD) error-types
- Treatment target selection within a range of evidence-based intervention approaches
- Rationales for and implementation of 8 traditional approaches to therapy target selection
- Rationales for, and implementation of, 8 newer approaches to therapy target selection
- Application of non-linear principles in intervention for syllable structure errors
- Application of complexity principles in treatment target selection
- Using facilitative articulatory contexts
This CPD offering has been designed with experienced through to novice clinical Speech-Language Pathologists/Speech and Language Therapists, SLP/SLT Clinical Educators and Instructors, and SLP/SLT Students in mind.

The 'Lighthouse Page' for Sound Reasoning
(5) Evidence-Based Intervention for Children with Speech Sound Disorders
ABOUT THIS 1-DAY or 2-DAY EVENT, new in 2015 and progressively updated for 2016-2021
'Evidence-Based Intervention for Children with Speech Sound Disorders' can be run as a 1-day or 2-day event and is designed for experienced through to novice Speech-Language Pathologists / Speech and Language Therapists, and SLP/SLT Students.
The range of evidence-based and/or theoretically sound intervention approaches SLPs/SLTs employ to work with children with SSD is extensive. They include: Auditory Input Therapy / Naturalistic Intervention, Core Vocabulary Therapy, the Cycles Phonological Patterns Approach, Dynamic Temporal and Tactile Cueing (DTTC), Imagery Therapy, Integral Stimulation, Metaphon, Parents and Children Together (PACT), Perceptually based intervention, Phoneme Awareness Intervention, Phonemic Intervention including four minimal pair approaches, Phonetic Intervention / Articulation Therapy, Psycholinguistic Intervention, Rapid Syllable Transition Training (ReST), Stimulability Therapy, The Multisensory Approach, The Nuffield Centre Dyspraxia Programme, and Vowel Remediation.
These approaches are described in detail in Bowen (2015). There are too many to cover in detail in one, or even two days, so Dr Bowen will work with hosts to choose their preferred interventions to meet the learning needs of participants, along with the assessment procedures and target selection strategies that are congruent with the chosen intervention approaches.
REFERENCE
Bowen, C. (2015). Children's Speech Sound Disorders (2nd ed). Oxford, Wiley-Blackwell.
(6) Addressing Children's Speech Sound Disorders: What’s under the Umbrella? (new for 2020-2021)
Topic
Speech-Language Pathologists / Speech and Language Therapists (SLPs/SLTs) who work with children with speech sound disorders (SSD) know that their difficulties can sometimes be relatively easy to assess and plan treatment for, and their intervention proceeds predictably, with a good speech outcome comparatively quickly. Alongside these “straightforward” children are those with more complex presentations that give SLPs/SLTs the opportunity to dig deep into the therapy toolkit, and sometimes relevant literature, to plan and deliver explicitly principled therapy, finely tailored to the client’s needs, monitored continually and modified if necessary, as intervention progresses. With either group, the SLP/SLT has a wide repertoire of assessment tools, and treatment approaches, procedures, activities target selection strategies to draw on—and these are associated with various levels of evidence.
This Continuing Professional Development (CPD) event starts with the basics of description, classification and identification of SSD; next, it covers a core speech assessment battery and the additional evaluation procedures that are often helpful when diagnosis is complicated; then on to target selection; and finally, intervention. READ MORE HERE
(7) Treatment Fads: Science and Pseudoscience in the Clinic and Classroom (new for 2019-2021)
Medicine and allied health are science-based professions in which ethical, evidence-based, theoretically sound practice is central. Nonetheless, pseudoscientific 'interventions' impact practice, complicating our work with children and young people with developmental disorders that affect aspects of speech, language, literacy, fluency, voice, communication, attention, cognition, working memory, behaviour, and nutrition.
In their book Making Sense of Interventions for Children with Developmental Disorders, Bowen and Snow (2017) clarify why pseudoscientific, “alternative” treatments don't or won't work, and in some instances why they are unsafe. But the book is not only about debunking myths and illuminating false promises. The authors also pilot readers towards treatments with worthwhile credentials, underpinned by solid theory, good science and common sense.
Drawing on the 2017 book, and ongoing research for books in preparation for 2021 and 2022, Dr Bowen aims to provide opportunities for participants to call on their information literacy and research literacy skills. Using these skills, they will
- review popular but troubling fad interventions;
- contrast them with interventions supported by robust research data;
- consider the cognitive biases that sustain them;
- look at fad-related, anonymized ethical dilemmas within four ethical frameworks;
- reflect on the opportunity costs for all concerned; and
- discuss what SLPs/SLTs might do and say in such potentially delicate situations.
The day comprises lecture-style content, small- and whole-group Q&A, discussion, and problem-solving around real but anonymized case scenarios. Participants are encouraged to recount fictionalized 'cases' of their own personal experience of, and responses to, questionable treatments.
Learner Outcomes: Participants will
Recognise the threats to clients, practice and the professions, posed by treatment fads.
Review key issues around research literacy, information literacy, and cognitive bias.
Contrast scientific interventions, with good credentials, with pseudoscientific, fad interventions.
Apply four frameworks to problem-solving ethical dilemmas, and learn from shared experiences.
Formulate responses to and remedies for ethical dilemmas, in Allied Health, and Education.
References
Bowen, C. & Snow, P. (2017). Making Sense of Interventions for Children with Developmental Disorders. Guildford: J&R Press.
Bowen, C., Snow, P., & Brandon, P. (in preparation for 2024). The Developmental Disorders Roadmap for Families and Teachers, Guildford: J&R Press.
Bowen, C. & Snow, P. (in preparation for 2025). Making Sense of Interventions for Children with Developmental Disorders, Second edition. Guildford: J&R Press.
The three books have a Twitter handle @TxChoices.
Page 1 of 2